On November 20,
1985, Windows 1.0 published. Bill Gates says, “It is unique
software designed for the serious PC user.” There are drop-down menus, scroll
bars, icons, and dialog boxes that make programs easier to learn and use.
You're able to switch among several programs without having to quit and restart
each one.
1987–1990 Windows 2.0–2.11 More windows, more speed
On December 9, 1987 Microsoft
releases Windows 2.0 with desktop icons andexpanded memory. With improved
graphics support, you can now overlap window

res2.windows.microsoft.com
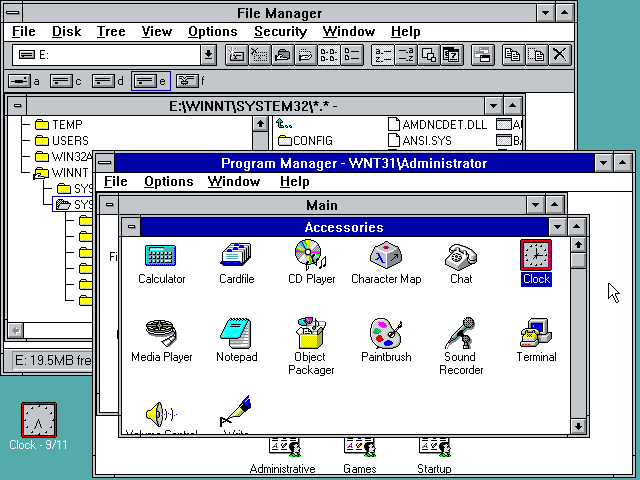
1990–1994 Windows 3.0–Windows NT—Getting the graphics
On May 22, 1990, Microsoft announces Windows 3.0, followed
shortly by Windows 3.1 in 1992. Taken together, they sell 10 million
copies in their first two years, making this the most widely used Windows
operating system yet. The scale of this success causes Microsoft to revise
earlier plans. Virtual Memory improves visual graphics. In 1990 Windows starts
to look like the versions to come.
res2.windows.microsoft.com
Windows now has significantly better performance, advanced graphics with 16 colors, and improved icons. A new wave of 386 PCs helps drive the popularity of Windows 3.0. With full support for the Intel 386 processor, programs run noticeably faster. Program Manager, File Manager, and Print Manager arrive in Windows 3.0.
res2.windows.microsoft.com
Windows 95 The PC comes of age
On August 24, 1995, Microsoft releases Windows 95, selling a record-setting
7 million copies in the first five weeks. It’s the most publicized launch
Microsoft has ever taken on. Television commercials feature the Rolling Stones
singing "Start Me Up" over images of the new Start button. The press
release simply begins: “It’s here.
This is the era of fax/modems, email, the new
online world, and dazzling multimedia games and educational software.
Windows 95 has built-in Internet support, dial-up networking, and new Plug
and Play capabilities that make it easy to install hardware and software. The
32-bit operating system also offers enhanced multimedia capabilities, more
powerful features for mobile computing, and integrated networking.


res2.windows.microsoft.com
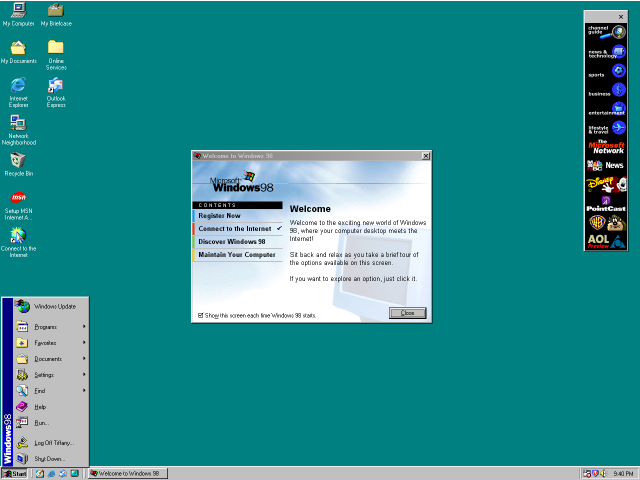
1998–2000 Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows Me | Windows evolves for work
Released on June 25, 1998, Windows 98 is the first version of Windows
designed specifically for consumers. PCs are common at work and home, and
Internet cafes where you can get online are popping up. Windows 98 is
described as an operating system that “Works Better, Plays Better.
With Windows 98, you can find information more easily on your PC as
well as the Internet. Other improvements include the ability to open and close
programs more quickly, and support for reading DVD discs and universal serial
bus (USB) devices. Another first appearance is the Quick Launch bar, which lets
you run programs without having to browse the Start menu or look for them on
the desktop.
res2.windows.microsoft.com
2001–2005Windows XP—Stable,
usable, and fast
On October 25, 2001, Windows XP is released with a redesigned look and
feel that's centered on usability and a unified Help and Support services
center. It’s available in 25 languages. From the mid-1970s until the release of
Windows XP, about 1 billion PCs have been shipped worldwide.
For Microsoft, Windows XP will become one of its best-selling products
in the coming years. It’s both fast and stable. Navigating the Start menu,
taskbar, and Control Panel are more intuitive. Awareness of computer viruses
and hackers increases, but fears are to a certain extent calmed by the online
delivery of security updates. Consumers begin to understand warnings about
suspicious attachments and viruses. There’s more emphasis on Help and Support.

res2.windows.microsoft.com
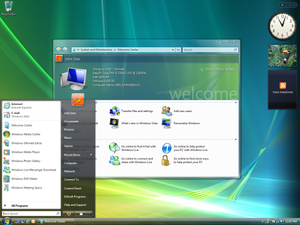
2006–2008Windows
Vista—Smart on security
Windows Vista is released in 2006 with the
strongest security system yet. User Account Control helps prevent potentially
harmful software from making changes to your computer. In Windows Vista
Ultimate, BitLocker Drive Encryption provides better data protection for your
computer, as laptop sales and security needs increase. Windows Vista also
features enhancements to Windows Media Player as more and more people come
to see their PCs as central locations for digital media. Here you can watch
television, view and send photographs, and edit videos.
res2.windows.microsoft.com
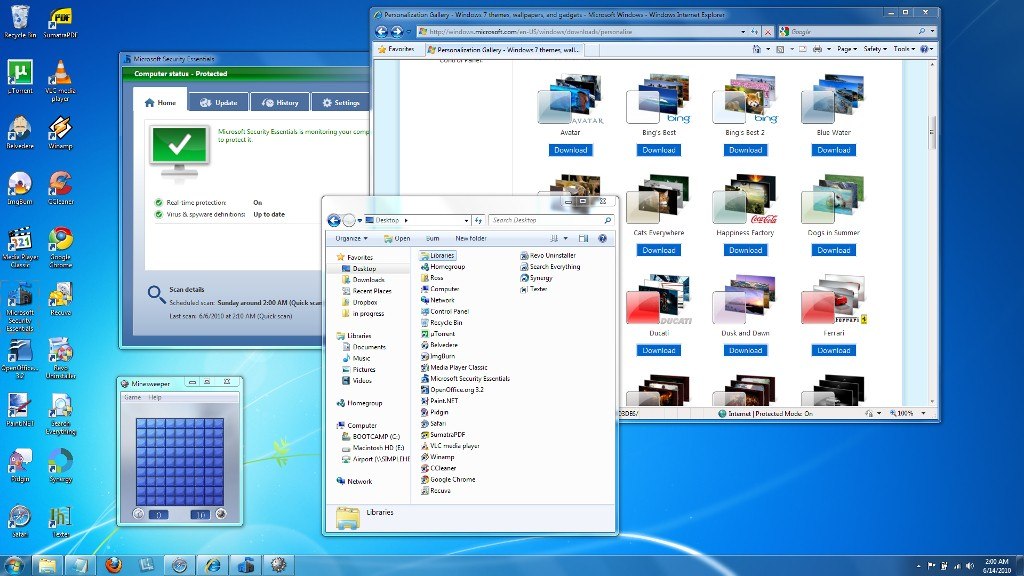
Windows 7 | Introduces Windows Touch
Windows 7 is released for the wireless world of the late 2000s.
Laptops are outselling desktops, and it's become common to connect to public
wireless hotspots in coffee shops and private networks in the home.
Windows 7 includes new ways to work with windows—like Snap, Peek, and
Shake—that improves functionality and makes the interface more fun to use. It
also marks the debut of Windows Touch, which lets touchscreen users browse the
web, flip through photos, and open files and folders.
res2.windows.microsoft.com
2012Windows 8 | Features apps and tiles
Windows 8 is a reimagined
operating system, from the chipset to the user experience, and introduces a
totally new interface that works smoothly for both touch and mouse and
keyboard. It functions as both a tablet for entertainment and a full-featured
PC for getting things done. Windows 8 also
includes enhancements of the familiar Windows desktop, with a new taskbar and
streamlined file management.
Windows 8 features a Start screen
with tiles that connect to people, files, apps, and websites. Apps are front
and center, with access to a new place to get apps—the Windows Store—built
right in to the Start screen.
Along with Windows 8, Microsoft also
launches Windows RT, which runs on some tablets and PCs. Windows RT is designed for sleek devices and long
battery life, and exclusively runs apps from the Windows Store. It also comes
with a built-in version of Office that's optimized for touchscreens.
https://line.do
res2.windows.microsoft.com
2013Windows 8.1 | Expands the Windows 8
Windows 8.1 advances the Windows 8 vision
of providing a powerful collection of apps and cloud connectivity on great
devices; it’s everything people loved about Windows 8, plus
some enhancements.
Windows 8.1 combines Microsoft's vision of innovation with customer feedback
on Windows 8 to provide many improvements and new
features: more Start screen personalization options that sync across all
devices, the option to boot directly to the desktop, Bing Smart Search so you
can find what you're looking for across the PC or the web, a Start button to
navigate between the desktop and Start Screen, and more flexible options for
viewing multiple applications at once on one or all screens. There are also
several new built-in apps such as Bing Food & Drink, Bing Health &
Fitness, and great utility apps like Reading List, Calculator, and Alarms. Many
of the great apps shipped in Windows 8 are
back and even better, making your experience more enjoyable right from the
start.
In addition to these user
experience changes, Windows 8.1includes new and
improved features like Workplace Join and Work Folders that enable Windows
devices to connect more easily to corporate resources.
https://line.do
res2.windows.microsoft.com
Windows 10
Unlike previous versions of Windows, Microsoft has
branded Windows 10 as a "service" that receives ongoing "feature
updates".
Windows 10 introduces what Microsoft described as
"universal apps"; expanding on Metro-style apps, these apps can be
designed to run across multiple Microsoft product families with nearly
identical code—including PCs, tablets, smartphones, embedded systems, Xbox
One, Surface Hub and Mixed Reality. The Windows user interface was revised to
handle transitions between a mouse-oriented interface and a
touchscreen-optimized interface based on available input devices—particularly
on 2-in-1 PCs; both interfaces include an updated Start menu which incorporates
elements of Windows 7's traditional Start menu with the tiles of Windows 8. The
first release of Windows 10 also introduces a virtual desktop system, a window
and desktop management feature called Task View, the Microsoft Edge web
browser, support for fingerprint and face recognition login, new security
features for enterprise environments, and DirectX 12 and WDDM 2.0 to improve
the operating system's graphics capabilities for games.
https://en.wikipedia.org


No comments:
Post a Comment